This is Scientific American's 60-second Science, I'm Jim Daley.
(Audio of magnetosphere)
That strange sound? It's Earth's magnetosphere—the magnetic field created by the movement of the iron core deep within the planet. The magnetosphere is a shield, protecting us from dangerous cosmic rays. And it vibrates like a drum when jets of charged particles from the sun, called plasma, crash into it.
The theory describing this phenomenon was developed in the 1970s. But it wasn't until recently that we had the tools to observe it. In 2007 NASA launched five satellites to study the magnetosphere, in a mission called Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, or THEMIS.
"We ended up making use of all five NASA THEMIS probes back very early in the mission, actually, when they were almost in a perfectly straight line."
Martin Archer, professor of physics and astronomy at Queen Mary University of London.
"And that was really ideal for trying to tease apart exactly what happens when something impulsive hits our magnetosphere."
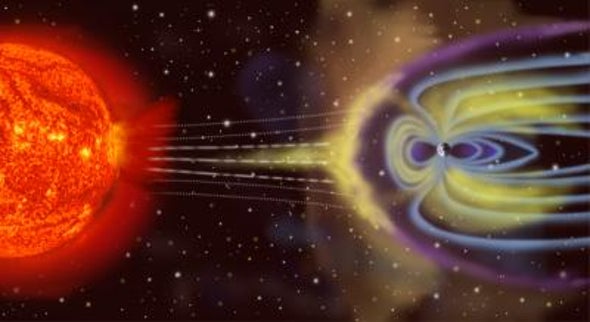
"So basically, what happened in this particular event is really quite simple. You had a jet of plasma traveling very fast that impacted on the magnetopoles—that's the boundary of our magnetosphere. That then sent out ripples in all directions. Now, some of those will then travel toward the north and southern poles and get reflected back, and it's the interference of the original and reflected waves that allows the standing waves to form very much like the surface of a drum. And that gives it a very well-defined frequency."
Archer's team converted the signals collected by the probes into audio that we can hear. They published the discovery in the journal Nature Communications.
"From the theory behind these drumlike oscillations, we know that they should have a big effect. They should penetrate our magnetic shield quite far, causing motions within regions where there are the radiation belts, for instance. Certainly, we saw perturbations on the ground in the magnetic field and that tells us that the ionosphere is moving as well, just in the same way as the boundary is, so it's like one side of the magnetosphere is just all ringing because of this mode."
These events occur on a colossal scale—the magnetosphere extends outward about 10 times the diameter of the earth. Archer's team has proposed that future studies look into ground-based sensing methods that can reveal more about the magnetosphere's behavior. Perhaps there's an important upside in better understanding our planetary shield.
Thanks for listening for Scientific American — 60-Second Science. I'm Jim Daley.












