So you're probably feeling pretty comfortable with the diagram of the heart,
大家已经熟悉了心脏的构造图
but let me just go ahead and label a few things,
这里我们再介绍一些名词
just to make sure we're all on the same page.
加深大家对心脏构成的理解
Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle,
血液从右心房到右心室
then it goes to the lungs and then the left atrium to the left ventricle.
然后进入肺,而后进入左心房,回到左心室
So that's usually the flow of blood.
这就是血液流动路线
And one of the things that keeps the blood flowing in the right direction we know is the valves.
而保证血液顺流,方向不出错的就是瓣膜
Two of the valves I'm actually going to name, I'll give you new names,
给大家介绍两个瓣膜的新术语
something slightly different from what we've been referring to them by
跟之前介绍的略微不同
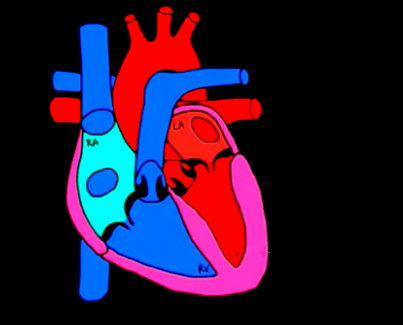
These are the atrioventricular valves.
这些都叫房室瓣
You can take a guess as to which ones I'm referring to.
大家可以想一下,房室瓣指的是哪些
Atrioventricular valves are the two valves between the atria and the ventricles.
房室瓣指的就是心房和心室之间的两个瓣膜
One will be the tricuspid valve and the other the mitral valve.
一个是三尖瓣,一个是二尖瓣
And just to orientate us:
标记一下
this is the tricuspid, the T; and this is our mitral, our M.
三尖瓣用T标记,二尖瓣用M标记
And the atrioventricular valves, these two valves
大家看这些房室瓣
if you look at them, they're both kind of facing downwards.
看起来是面朝下的
And one of the things that you might be wondering is
大家可能会想
'How is it that they aren't just flopping back and forth?'
为什么这两个瓣膜不会被血液冲得前后运动呢?
And these valves in particular have a very interesting strategy,
这些瓣膜,有一个特征
and that is that they're actually tethered- they are tethered to the walls.
它们其实是附着在心脏壁上的
So they're held down here, like that.
像这样
And they have on the other end of those tethers, a little muscle there.
另一端也有一小块肌肉附着在心脏壁上
Now this makes perfect sense if you think about it.
大家想一下,这是非常合理的
Because the ventricles are very strong, right?
大家都知道,心室是非常有力的
We know the ventricles are really really strong.
是强有力的
And so if the ventricles are squeezing,
如果心室挤压室内血液
there's a good chance the blood is going to shoot up in any direction it can go. Right?
那么很有可能血液要向各个方向流散
It's going to go back perhaps through the mitral valve,
可能会通过二尖瓣
it can go there, or it'll go through the tricuspid valve, if it can go there.
又或者可能的话,通过三尖瓣
But the reason that it won't, is that these papillary muscles are basically kind of sending out little life lines,
但之所以不会逆流,就是因为这些乳突肌
these chordae tendinae life lines to keep the valve from flipping backwards.
这些腱索阻止了血液回流
So these chordae tendinae, these cords are important for that reason. Right?
所以这些腱索是非常重要的
They keep the valve from flipping backwards.
阻止了血液的回流
So these are all the chordae tendinae and these are the papillary muscles
这些是腱索,这些是乳突肌
And these are particularly important and we can tell for when you're trying to make sure that the ventricles don't screw up the valves.
这些是非常重要的,确保心室血液不会回流
And now let's say that by accident our ventricle was just too strong, too powerful,
假设心室力量太大
let's say it broke one of these cords.
假设把其中一条腱索拉断了
Let's say it broke this one right here.
假设把这条拉断了
And that's because our ventricle was just forcing too much blood back and it just snapped the cord.
因为心室要把血液全部挤压出去,可能拉断了一条腱索
What would happen?
这时会发生什么呢?
This would basically kind of start flipping back and forth,
可能瓣膜抵抗不了血液冲击了
it would flip this way and this way.
可能会像这样上下移动
And then on the next heartbeat, blood would start going the wrong direction, right?
那么在下次心跳中,血液就可能逆流
Because this valve is not able to keep that nice tight seal.
因为瓣膜不能完全关闭了
And so blood would basically kind of go this way when it wasn't supposed to.
所以血液可能出现逆流的情况
And all of a sudden our flow of blood is now going in the wrong direction.
血液可能会逆流
So the chordae tendinae and the papillary muscles do a really really important job in preventing that from happening.
因此,这些腱索和乳突肌起到了防止血液逆流的关键作用











